Subinterfaces let you split one physical network port into multiple logical interfaces. Each subinterface can carry its own VLAN tag (802.1Q), IP addressing, and access control rules — enabling inter‑VLAN routing and efficient hardware use.
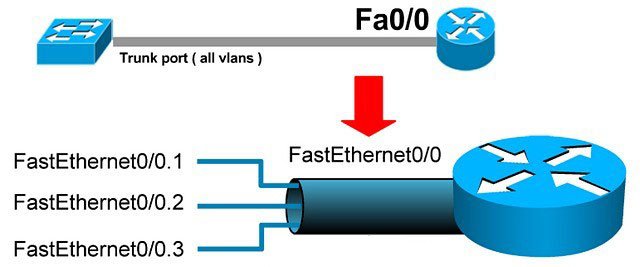
What is a Subinterface?
A subinterface is a logical interface created on a physical interface of a router or firewall. It behaves like a separate network interface with its own IP address and configuration. Common naming follows vendor conventions, for example GigabitEthernet0/0.10 for VLAN 10 on Cisco devices.
How Subinterfaces Work
On trunk links, frames are tagged with a VLAN ID using 802.1Q. The router inspects the tag and passes traffic to the matching subinterface. This architecture is often called Router‑on‑a‑Stick.
Benefits and Use Cases
- Inter‑VLAN routing using a single physical interface.
- Cost savings — fewer physical interfaces and modules required.
- Flexible segmentation with per‑VLAN policies, DHCP scopes, and ACLs.
- Common in enterprise, campus, and multi‑tenant ISP networks.
Cisco Configuration Example (Router‑on‑a‑Stick)
Cisco IOS sample
! Bring up the physical interface
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
no shutdown
! Subinterface for VLAN 10
interface GigabitEthernet0/0.10
encapsulation dot1Q 10
ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
! Subinterface for VLAN 20
interface GigabitEthernet0/0.20
encapsulation dot1Q 20
ip address 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0
! Subinterface for VLAN 30
interface GigabitEthernet0/0.30
encapsulation dot1Q 30
ip address 192.168.30.1 255.255.255.0Best Practices
- Use descriptive naming and document VLAN IDs and IP schemes.
- Apply ACLs on subinterfaces to limit inter‑VLAN access where needed.
- Monitor trunk links for bandwidth and use QoS if carrying many VLANs.
- For high throughput, consider using multiple physical links or SVI (switch virtual interfaces) on L3 switches.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the purpose of a subinterface?
- To allow multiple VLANs or logical networks to share a single physical interface for routing or segmentation.
2. Can subinterfaces have different IP networks?
- Yes — each subinterface can be assigned its own IP address and subnet.
3. Are subinterfaces vendor specific?
- The concept is vendor agnostic, but syntax and capabilities vary. Cisco, Juniper, Fortinet, MikroTik, and others support similar mechanisms.
Comments (0)
Leave a Comment
No comments yet. Be the first to comment!